What is Menorrhagia
Menorrhagia is a disorder in the female menstrual cycle. It causes heavy menstrual bleeding. There are several menstrual cycle disorders other than Menorrhagia.
- Some of those are,
- dysmenorrhea,
- amenorrhea/ oligomenorrhea, and
- post-menopausal bleeding.
If women bleed more than 80ml per day in her menstruation, it can consider as Menorrhagia. But it is challenging to measure menstrual blood loss correctly. So women have to identify heavy menstruation by themselves.
In Menorrhagia, women may experience,
- presence of blood clots with period
- soaked sanitary wears need to be changed frequently, and the
- bleeding is flooding,
- blood spills over the sanitary towel and on to the pants, clothes, or bedding.
- due to the heavy bleeding need to take off from work.
Causes of Menorrhagia
- Fibroids-fibroids
- It is a noncancerous growth in or around the uterus. Having fibroids increase the surface area of the uterus. So it helps to cause heavy menstruation in the period.
- Endometrial polyps
- It is also a noncarcinogenic growth in the inner lining of the uterus, and it contributes to menstruation, similar to Fibroids-fibroids.
- Coagulation disorders
- Diseases that disrupt blood clotting is known as Coagulation disorders.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- This disease is caused as a result of bacterial infection in the upper part of the female reproductive system.
- Thyroid disease
- Thyroid glands produce important hormones that regulate body metabolism. The thyroid hormone is one of them, and it helps to control the menstrual cycle.
- Drug therapy like warfarin
- Warfarin is an anticoagulant (blood thinner).
- Use of intrauterine contraceptive (IUD) device.
- IUD is an effective nonsurgical option for pregnancy prevention.
- Endometrial, cervical carcinoma
- In Endometrial cancer, several types of malignancies develop in uterus inner lining cells.
- Cervical cancer occurs in the cells of the cervix.
How to diagnose Menorrhagia
For diagnose Menorrhagia, there are several investigations used combining the patient history and symptoms.
Investigations use to diagnose
- FBC
- Full blood count (FBC) helps to view the hemoglobin count. It indicates the blood level in the body. If it is low, that means a lot of blood has already bled.
- Coagulation screen
- The coagulation screen test can identify the presence of blood clotting disorders.
- Pelvic ultrasound scan
- If there is a pelvic mass presence when palpating the abdomen, a pelvic ultrasound scan will be done to identify whether the mass is a fibroid or not.
- Also, the scan is done when irregular or intermenstrual bleeding presence to exclude endometrial polyp.
- High vaginal and endocervical swabs
- High vaginal and endocervical swabs are taken if unusual vaginal discharge and risk factors for the pelvic inflammatory disease presence.
- Endometrial biopsy
- Endometrial biopsy is performed if all of the following conditions are met.
- women’s age is more than 45
- presence irregular or intermenstrual bleeding
- do not respond to the drug treatments
- In an endometrial biopsy, a small tissue sample from the uterus endometrium is taken using the pipelle endometrial sampler to examination under a microscope.
- If the above method failed to obtain Endometrial biopsy, under general anesthesia, an endometrial biopsy is performed with the aid of hysteroscopy.
- Endometrial biopsy is performed if all of the following conditions are met.
- Thyroid function tests
- Since the hormone produced in the thyroid glands directly affects the menstrual cycle, the functionality of the thyroid is tested using a series of blood tests.
Treatment for Menorrhagia
- There are two treatments for Menorrhagia. They are,
- medical treatment
- surgical treatment
Before selecting a treatment method, several factors need to consider. Because the method of treatment affected those factors.
- Those factors are
- the preferences of the patient about the treatment method
- whether the patient need contraception or not
- benefit and risk for the patient from the method of the treatment
- whether the patient has any past disease which will be contraindicated to the treatment method
1. Medical treatment
- Medical treatment can divide into non-hormonal and hormonal treatment.
- Hormonal treatment
- Combined oral contraceptives pills
- Norethisterone
- Levonorgestrel intrauterine system
- GnRH agonists
- Non-hormonal treatment
- Mefenamic acid and NSAID (non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs)
- Use of Tranexamic acid
- Hormonal treatment
i. Hormonal treatment
Combined oral contraceptive pills
These pills have estrogen. Excess estrogen causes to suppress pituitary gonadotropin release. Lack of gonadotropin prevents ovulation from occurring.
The endometrium prepares lots of blood vessels to provide nutrients for the ovum, expecting that it will meet a sperm and grow into a fetus. If the ovum was unable to fertilize, the endometrium is broken and passe via the vagina. It is known as menstruation. Continuous use of the pills prevents ovulation and menstruation.
- The benefit of the combined oral contraceptive pills is,
- it gives effective contraception.
- The disadvantages are,
- it increases the thromboembolism,
- increase the risk of breast cancer in patients who have a family history of breast cancer,
- gains overweight
Norethisterone
Progesterone is a hormone released by the ovaries. Norethisterone is a type of synthetic progesterone. It stops uterus lining from the shedding. Usually, the progesterone level is increased in pregnancy. It keeps the fetus in the uterus without letting to shed endometrium. So, it helps in maintaining pregnancy. Using norethisterone lead to stop menstruation without pregnancy.
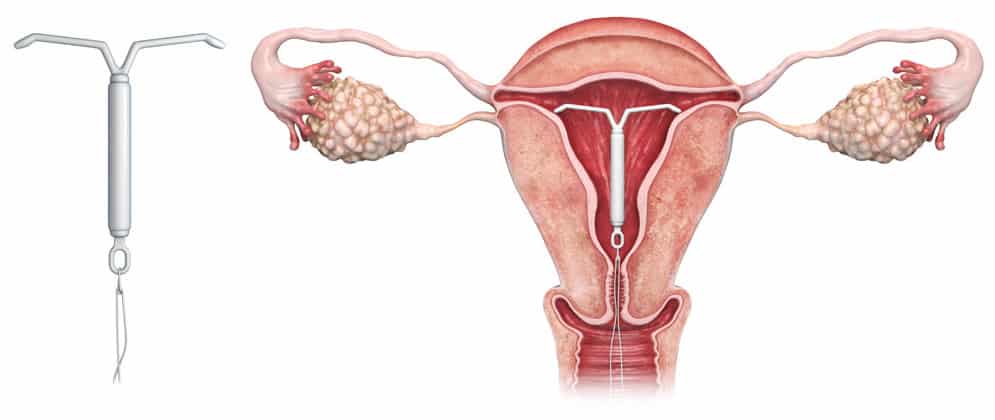
Levonorgestrel intrauterine device
Levonorgestrel intrauterine device releases levonorgestrel. It is similar to progesterone. It targets endometrium directly. High levonorgestrel level causes to suppress endometrial proliferation. So shedding of the thin epithelium in the endometrium does not cause heavy menstruation.
- The benefits of using levonorgestrel IUCD are
- contraception,
- it reduces the effect for the dysmenorrhoea (painful menses),
- amenorrhea (no menstruation) after insertion.
- disadvantages are
- irregular menses and
- breakthrough bleeding for the first three to nine months after the insertion.
GnRH agonist
This drug act like the GnRH hormone. So it acts on the pituitary gland and stops the production of estrogen. Lack of estrogen cause amenorrhea (no menstruation).
- The advantage of using this is,
- it is effective for dysmenorrhoea
- Disadvantages are,
- irregular bleeding,
- flushing,
- mood changes and
- sweating due to the lack of body estrogen
It is not suitable to use for more than 6 months. Using it for more than six months causes the development of the hypoestrogenic state (estrogen deficiency). Estrogen prevents the breakdown of the bones. So a lack of estrogen develops osteoporosis.
ii. Non-hormonal treatment
Mefenamic acid and Non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs
These drugs reduce the production of prostaglandins. The action of prostaglandin for heavy menstruation is still unclear. But mefenamic and NSAID cause a decrease in the amount of blood in menstruation.
- The benefits of these drugs are,
- it decreases the pain
- Disadvantages are,
- it causes gastric and duodenal ulcers, and lead to severe gastritis.
Tranexamic acid
Tranexamic acid helps to form blood clots, and it helps to decrease the bleeding.
2. Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment for Menorrhagia uses endometrial ablation and hysterectomy (removing uterus). But if women need to preserve her fertility (ability to conceive), medical treatment is the option.
Endometrial ablation
In endometrial ablation, the full thickness of the endometrium ablated by the controlled application of energy. The form of energy can either be heat or microwaves.
- Performing endometrial ablation,
- 40% percent will become amenorrheic.
- 40 % reduced blood loss in menstruation.
- 20% will experience not differ in their bleeding.
- The disadvantages in this method are
- hemorrhage ( bleeding),
- uterine perforation.
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is an operation that removes the whole uterus. It completely cures the bleeding from the uterus.


Pingback: Menstruation Process Phases of Your Cycle - MedFog
Pingback: What are Fibroids - Symptoms of fibroids, types, and treatments